| 일 | 월 | 화 | 수 | 목 | 금 | 토 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | |||
| 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 |
| 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 |
| 19 | 20 | 21 | 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 |
| 26 | 27 | 28 | 29 | 30 | 31 |
- FineGrained
- classification
- computervision
- 머신러닝
- REACT
- nerf
- Python
- nlp
- clean code
- ML
- Torch
- GAN
- dl
- 딥러닝
- Vision
- algorithm
- PRML
- Front
- SSL
- math
- Depth estimation
- 3d
- Meta Learning
- FGVC
- cs
- 알고리즘
- 자료구조
- CV
- web
- pytorch
- Today
- Total
KalelPark's LAB
[ Computer Vision ] All about Activation Function 본문

All about Activation Function
- 입력 신호의 총합을 출력 신호로 변환하는 함수를 말합니다.
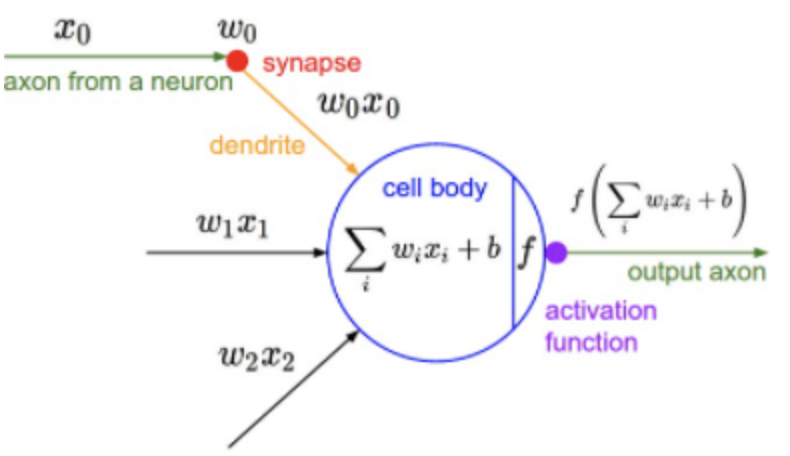
- 활성화 함수가 비선형 함수여야 하는 이유?
- 인공 신경망에서 선형 함수를 이용하면, 신경망의 층을 깊게하는 의미가 없습니다.
그러므로, 층을 쌓기 위해서는 비선형 함수인 활성화 함수(Activation Function)를 사용해야 됩니다.
Sigmoid
import numpy as np
def sigmoid(x):
return 1 / (1 + np.exp(-x))- Logistic Regression이라고도, 불린다.
일반적으로 활용되는 활성화 함수이며, [0, 1]의 범위를 갖습니다.
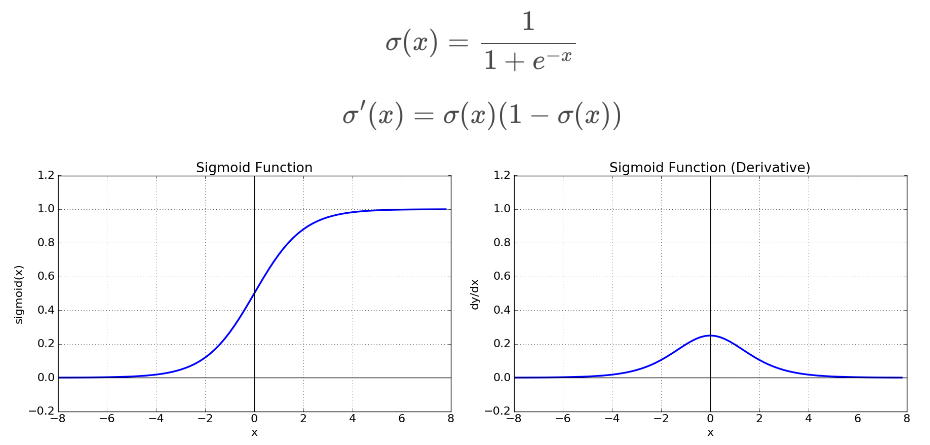
단점
- Gradient Vanishing 현상이 발생합니다. 미분 함수에 대해서 | x | 값이 커질수록 미분 값이 0에 수렴
tanh (Hyperbolic tangent)
import numpy as np
def tanh(x):
return (np.exp(x) - np.exp(-x)) / (np.exp(x) + np.exp(-x))- logistic function처럼 연속적으로 미분 가능하다. [-1, 1]의 범위를 갖습니다.
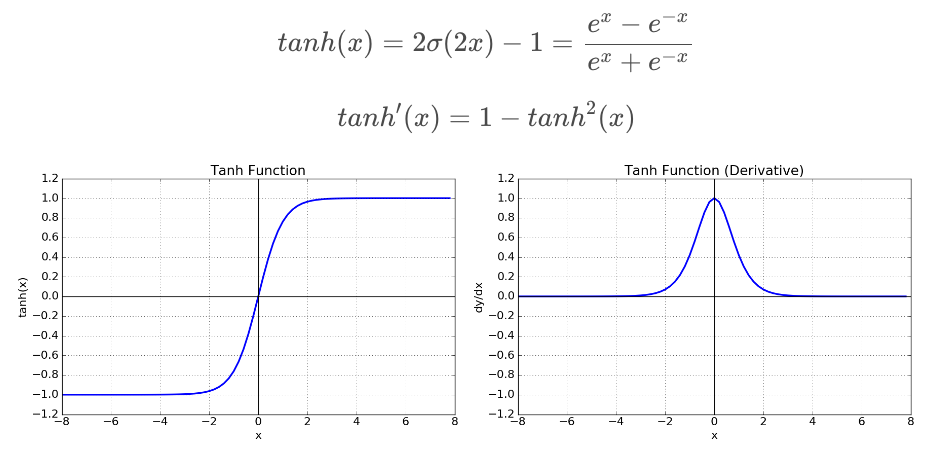
단점
- Gradient Vanishing 현상이 발생합니다. 미분 함수에 대해서 | x | 값이 커질수록 미분 값이 0에 수렴
ReLU (Rectified Linear)
import numpy as np
def relu(x):
return max(0, x)
- 연속이지만, x = 0에서 미분이 불가능합니다. (음수의 경우 0을 출력하기에, 계산 속도가 상당히 빠르다는 이점이 존재)

단점
- x < 0인 값들에 대해서 기울기가 0이기 때문에, 0이외의 값을 출력하지 않는다는 의미에서 죽었다라고 하며,
죽은 ReLU라고 한다.
LeakyReLU
- ReLU의 뉴런이 죽는 현상을 해결하기 위하여, 나온 함수
import numpy as np
def leakyrelu(a, x):
return a*x if x < 0 else x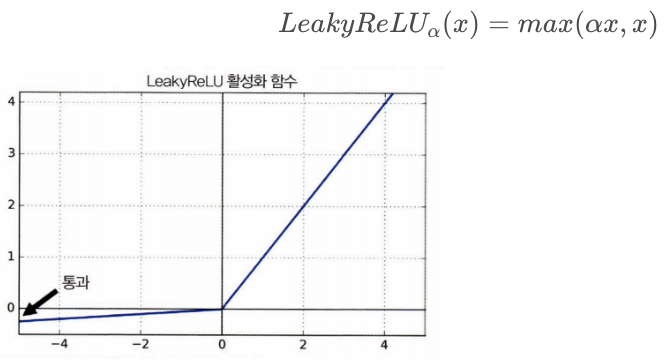
PReLU(PRametric Leaky ReLU)
import torch.nn as nn
class PReLU(nn.Module):
__constants__ = ["num_parameters"]
num_parameters : int
def __init__(self, num_parameters : int = 1, init : float = 0.25,
device = None, dtype = None) -> None:
factory_kwargs = {"device" : device, "dtype" : dtype}
self.num_parameters = num_parameters
super(PReLU, self).__init__()
self.weight = Parameter(torch.empty(num_parameters, **factory_kwargs).fill_(init))
def forward(self, input : Tensor) -> Tensor:
return F.prelu(input, self.weight)
def extra_repr(self) -> str:
return 'num_parameters={}'.format(self.num_parameters)- a가 훈련하는 동안 학습되는 방법입니다. (하이퍼파라미터는 아니지만, 다른 모델 파라미터와 마찬가지로, 역전파에 의한 변환)
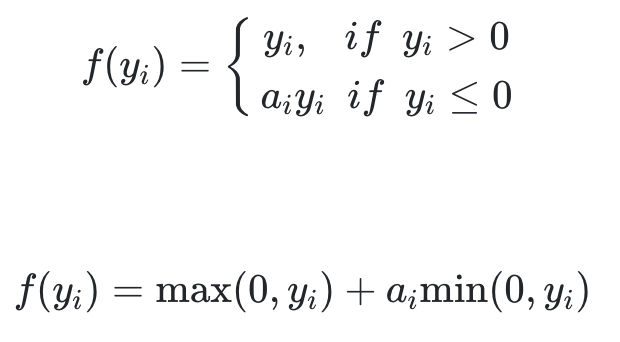
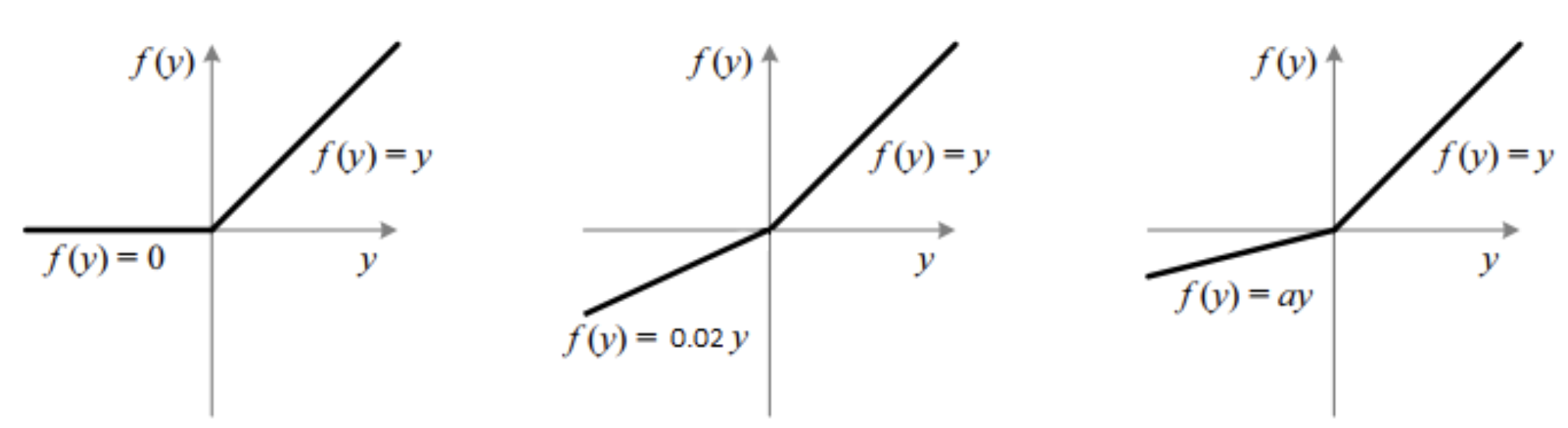
단점
- 대규모 Dataset에서는 유용하지만, 소규모 Dataset에서는 overfitting 위험이 존재.
ELU(Exponential Linear Unit)
import numpy as np
def elu(a, x):
return a*(np.exp(x) - 1) if x < 0 else x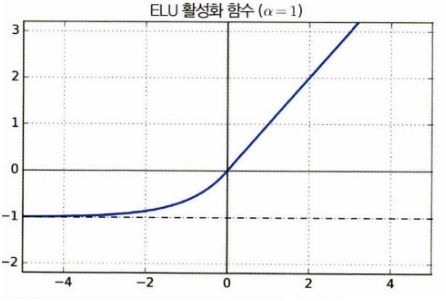
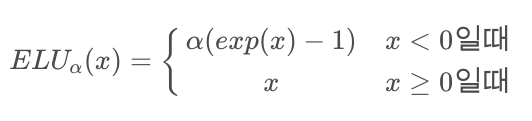
SELU(Scaled ELU)
- ELU의 활성화 함수의 변종
- 완전 연결 층만 쌓고, 모든 은닉층이 SELU 활성화 하수를 사용하면, 자기 정규화(self-normalized)가 된다고 주장
import numpy as np
def selu(x, alpha = 1, scale = 1):
return np.where(x <= 0, scale * alpha * (np.exp(x) -1 ), scale * x)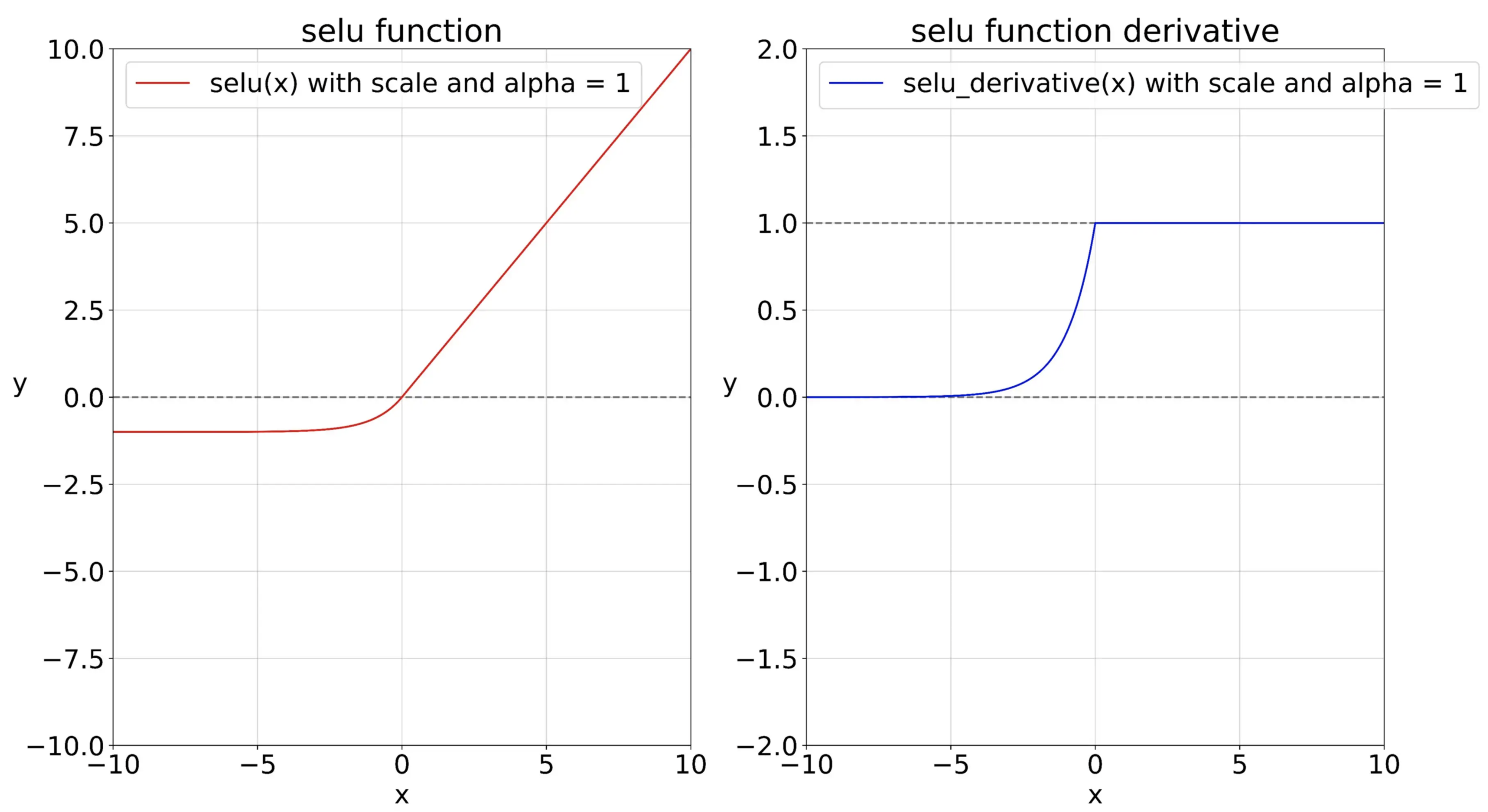
Maxout
import numpy as np
def maxout(x):
return max(np.dot(w_1, x ) + b_1, np.dot(w_2, x ) + b_2)- RELU가 가진, 모든 장점을 가졌습니다. 단점으로는 계산량이 복잡
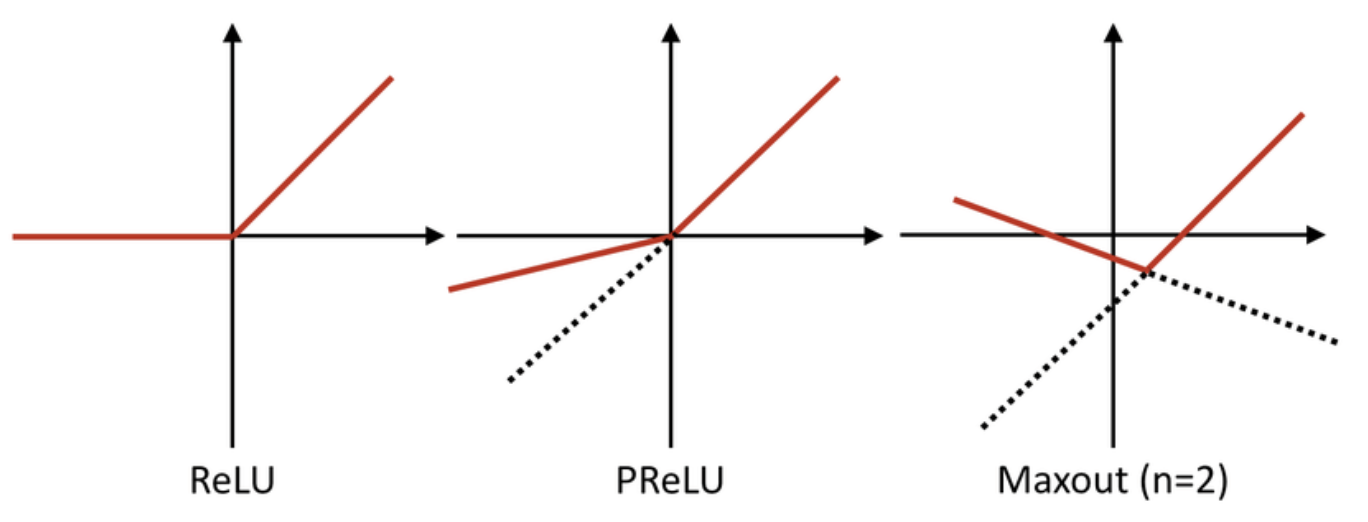
GELU(Gaussian Error Linear Unit)
import numpy as np
def gelu(x):
x = (((2 / np.pi) ** 1/2) *(x + 0.44715*(x **3)))
return 0.5*x*(1 + ((np.exp(x) - np.exp(-x))/(np.exp(x) + np.exp(-x))))- RELU가 가진, 모든 장점을 가졌습니다. 단점으로는 계산량이 복잡
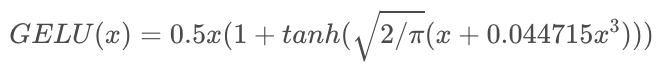
Activation function Tip
- 일반적으로 SELU > ELU > LeakyReLU > ReLU > tanh > sigmoid 순서 활용
- 실행속도가 중요하다면, LeakyReLU를 활용합니다.
- Dataset의 크기에 따라, 크다면, PReLU가 적당합니다.
'Data Science > Common' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [ Computer Vision ] PSNR, SSIM이란? (0) | 2023.01.28 |
|---|---|
| [ Computer Vision ] Attention, Transformer 이해하기 (2) | 2023.01.14 |
| [ Computer Vision ] Siamese-ennead CNN이란? (0) | 2023.01.03 |
| [ Computer Vision ] All about Classification Metrics (0) | 2022.12.30 |
| [ Computer Vision ] Jigsaw Generator 구현 (0) | 2022.12.05 |




